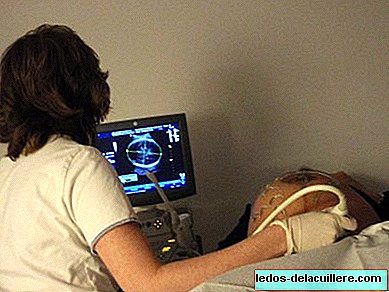
The Fetal Chromosomal Abnormalities Detection Program has been implemented in Asturian hospitals for approximately five years, through which they have been able to Detect almost 85% of cases of Down Syndrome through a screening test.
The screening test consists of a biochemical test and an ultrasound, without posing any risk to the fetus. From this screening, the risk of chromosomal alteration in the fetus is obtained and, therefore, it is determined whether or not some type of diagnostic test is needed, such as amniocentesis.
Screening is done during the first trimester of pregnancy. In the case of suspected high risk, amniocentesis is performed between the 12th and 16th weeks, while the chorion biopsy can be done in the 12th week, since the maximum early periods are considered without assume a high risk.
Of all the women who underwent the Program, in the vast majority of cases where there was some kind of chromosomal alteration, voluntary termination of pregnancy was chosen. In addition, it should be considered that these alterations generate a higher risk of miscarriage.
Currently, the aim is to increase the sensitivity of the screening to, in this way, decrease the use of invasive methods such as the aforementioned amniocentesis or chorion biopsy which pose risks to the fetus.