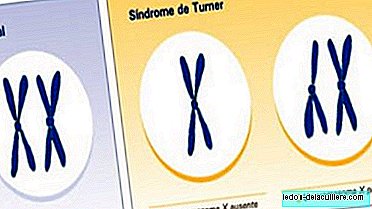
He Turner syndrome It is a genetic disease that only women suffer. It happens that their cells do not have the usual two XX chromosomes, but they lack an X or part of it.
This genetic problem is manifested primarily in short stature, lack of development of the ovaries and therefore, infertility. We will see in more detail the symptoms and treatment throughout the article. In infants, lymphatic edema in hands and feet is significant, one of the alerts that should always be consulted with the pediatrician if they manifest. An early diagnosis is essential.
It is a genetic problem of a relatively high frequency: one in 2,500 or 3,000 girls born alive It is a carrier of this anomaly that consists of the loss of one of the X chromosomes, that is, they have only 45 chromosomes instead of the 46 that are normal.
A third of girls with Turner syndrome They are identified shortly after birth. Approximately another third will be identified at school time by a striking short stature and the remaining third will be identified in adolescence or adulthood due to lack of pubertal development, lack of ovulation or infertility.
Half of the patients are completely 45, X but the other half have mosaicism, that is, some of their cells have the normal XX double chromosome and others do not. There are also cases in which the other cell line is 46, XY and 47, XXX and other variations. When one cell line is 46, XY and the other 45, X, the possibility of disorders is greater, especially in the genitals, both because of their masculine appearance and because of tumor problems.
It is also identified in 10% of natural abortions so it is a fairly frequent cause of pregnancy loss, and yet it is important that parents know that if they have had a daughter with Turner or have lost a pregnancy for this reason they have no more chance than any other couple that the problem is repeated.
Symptoms of Turner syndrome
Not all girls are equally affected by physical symptoms of Turner syndrome and there are many variations, influencing to a certain extent that they have 46, XX or not cell lines. A medical supervision is essential to attend each case in a personalized way.
The most obvious and widespread feature of this genetic problem is short stature. Women who suffer from Turner and are not treated are low and half of them will not reach 1.45. However, this is a minor problem.
It is more complicated to address the issue of sexual development, as a very low development of primary and secondary sexual characteristics is common, that is, their ovaries are stunted and may suffer from amenorrhea. This means that most have serious fertility problems or are sterile, although a little less than 2% of them get to conceive without help.
They are also characterized by other body manifestations such as the broad thorax, a deformation in the elbow (cubitus valgus), short and wide neck, very low hairline growth and lymphedema in the extremities, which is why carriers when they are babies in a third of cases.
Heart problems occur in a significant percentage of cases, especially in the aorta, so periodic checkups are usually done by the cardiologist in these cases.
To a lesser extent they present abnormalities in the position of the ears, deformity in the palate, scoliosis, droopy eyelid, strabismus, deafness and intolerance to carbohydrates.
Hypothyroidism occurs in 15-30% of patients. Control is usually maintained throughout childhood to measure thyroid function and will, therefore, be one of the analyzes that will be performed on all girls with short stature. In girls with Turner the controls should be carried out regardless of the size they are reaching to be able to treat them if there are inadequate hormone levels.
It is recommended to use growth hormone towards 5 years and always before 10 but in a personalized way and deciding in each family. In addition, most girls with Turner will need hormonal treatment to develop puberty and will still need it to maintain menstrual cycles.
Other problems related to Turner syndrome
In Turner syndrome it does not cause problems of mental retardation or autism in greater proportion than those that appear in the rest of the population but if you have to be attentive to particular psychological manifestations.
That is, there is no expression of the syndrome in psychiatric or neurological problems, but if the experiences of girls can cause problems and psychological suffering. The short stature, the poor development of sexual characteristics and the understanding of infertility make it necessary to be attentive to be able to refer the young person to mental health specialists since they are circumstances that can be very difficult to accept and assume without emotional pain.
Overprotection and concern for the girl are indicated as the cause of greater childishness and dependence, and also indicate pictures of anxiety, insecurity and school adaptation.
Adolescence can be very complicated for these girls and may, therefore, have trouble accepting their body and self-esteem scheme. In adulthood, a smaller proportion of them are indicated, forming stable partners and some sexual problems, but psychological issues are clearly influenced by experiences and surroundings.
Conclusion
He Turner syndrome It appears when the baby loses her second sex chromosome and will be a girl with some problems derived from this condition.
The short stature, the possible cardiac problems are the most important, highlighting also the lack of development of the ovaries and the non-production of sex hormones, which means that they do not get to present puberty without hormonal help in most cases.
For the rest, the girls with Turner syndrome, which are approximately one in 2,500 born, have a normal intelligence and good conditions of emotional life and health provided they receive the appropriate attention.
More information | Medicine and prevention In Babies and more | XXY, triple sex chromosome in males, Cat Meow Syndrome, Rare cases of twins